
In just a few decades, e-commerce has switched from basic online transactions to an emergency shopping experience from AI. With a rapid lead by 2025, the industry is currently in another important moment driven by ambitious technology and changing consumer preferences.
With the increasing prevalence of artificial intelligence (AI), hyper-personalized shopping experience and frictionless digital payment solutions, the way businesses and consumers transact online is transforming.
In this climate of cut-throat competition, E-commerce brands are forced to innovate to stay relevant. Today’s shoppers crave quick, intuitive, and personalized shopping expeditions as if they’re effortless, and that includes everything from search to product discovery to checkout. Online shopping has never been more exciting, with AI-powered chatbots offering customers assistance, and augmented reality (AR) allowing them to virtually try on products.
Moreover, the emergence of payment technology by digital wallets or adoption of crypto-currency or the burgeoning segment of buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services will continue to revolutionize transactions. Consumer expectations are changing, making it more difficult for businesses to stay up to date with the latest tech trends lest they risk losing market share to more nimble and techliterate competitors.
In this blog we will discuss some of the key innovations redefining the e-commerce evolution in 2025 and how businesses can adapt themselves to utilize these changes for an upper hand over the competition.
What is E-commerce?
E-commerce means purchasing and selling of items and services over the internet. It includes a variety of online purchases, retail sales, digital goods purchase, subscription services and internet banking. Whether they are small startups, medium-size local businesses, or large global enterprises, e-commerce platforms help businesses meet their customers, grow their market share, and improve operational performances.
As technology has evolved, so too e-commerce has transformed over and above your usual online store. Nowadays, it encompasses portable commerce (m-commerce) and social commerce, voice commerce, and AI-powered shopping encounters.
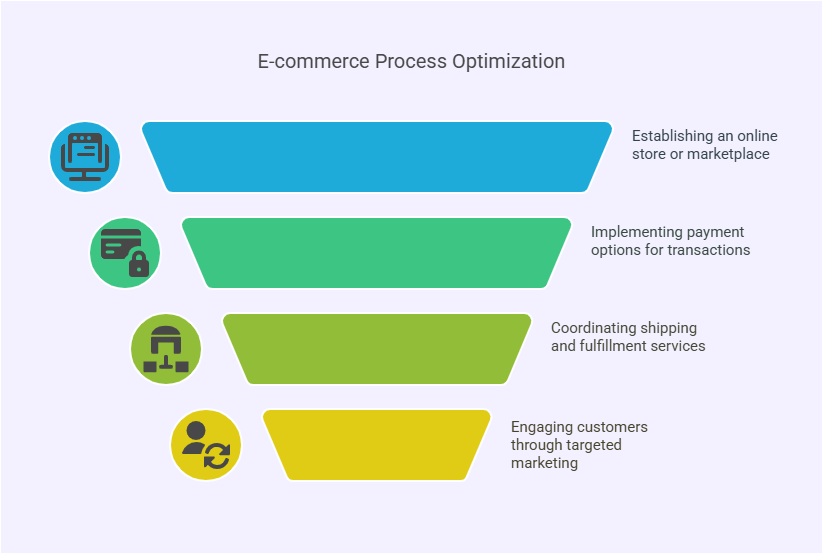
Key Components of E-commerce
- Online Stores & Markets: Amazon's site, Shopify stores, and Etsy all permit for online exchanges to require place.
- Installment Doors: Secure online installments made by means of PayPal, Stripe, Apple Pay, etc.
- Shipping & Fulfillment Processes: Warehousing, shipping still is necessary to fill an order smoothly for buyers.
- Marketing & Customer Engagement: AI-driven suggestions, email and digital marketing are all important factors in improving the customer's experience when they purchase products from your website.
The impact of e-commerce is verifiable, because it has changed how individuals shop by making exchanges less demanding, more convenient, and accessible to a around the world gathering of people.
History of E-commerce: The Evolution of Online Shopping
The e-commerce industry has grown from being dwarfed by everybody else to a mature multinatinal giant. in this article, however, we aim to take you through it s evolution over a number of decades.
The birth of e-commerce (1970s-1980s)
- The foundation of e-commerce was laid in the 1970s with EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) which allowed businesses to exchange documents between their computers.
- In 1979 Michael Aldrich invented online shopping. He connected a television set via telephone line to a transaction processing computer in real time, and founded a company named his back then—‘Hominis Lettro’.
The Rise of Online Shopping (1990s-Early 2000s)
- 1991: The Internet becomes publicly accessible and inevitably e-commerce is born.
- 1994: Staples did $8 million in sales online. Today, that number is $7.8 billion a month on average or an annual rate of over $94 billion online every year! And in 1995 he sold the first item over an Internet shopping system to one Mrs Jane Snowball Adams.
- Online book sales were so successful that in 1995 Jeff Bezos launched Amazon Bookselling Corporation on the World Wide Web where all kinds of new and used books could be purchased at discount price; he is now known as Amazon.com.
- The business was an immediate success with $ 20,000 worth of orders taken on its opening day alone Secretary place Viacom (then known as Viacom) was some trade association, providing space for Trading Grid members to display their products; but it was not actually an online store.
- This Futurist Building Tower across town from law firm Sidley and Austin, has been given free use of a 30X45 space on the 30th floor which they call ‘Trading Grid’ that will allow members to set up their own computer terminals -- all these services bundled into one by.
- Volume The dot-com crash of 2000 saw a rapid rise in the amount of internet-enabled retail, though as many early e-commerce ventures failed because their business models were simply not sustainable.
Mobile Commerce & Digital Revolution (2010s-Present)
- The rise of smartphones gave birth to m-commerce and mobile apps with which items could be purchased.
- In 2011 Google Wallet launched Apple Pay followed it in 2014 to help change the way people pay for things.
- The future, tailored product recommendations and personalized chatbot support. With AI we can now get exciting things like customized cups of coffee shipped right at our doorsteps.
The Future of E-commerce (2025 & Beyond)
- AI-powered shopping assistants and voice commerce (via Alexa, Siri) is finding its way into the mainstream.
- Augmented Reality (AR) enables people to see what they are buying before they make a purchase.
- Sound. Lastly, ethical and sustainable e-commerce is increasingly important these days. Brands are trying more and more to be eco-friendly; they want responsible sourcing for their products as well.
- Cryptocurrency & blockchain might further disrupt online transactions. Online shopping should be more secure and transparent.
- E-commerce has not only reinvented retail, but it has also transformed the global division of labor. The possibilities are boundless for the businessperson and customer alike.

Pros and Cons of E-commerce
E -commerce has changed the face of the market and the way consumers buy. But all commercial models, it has advantages and disadvantages.
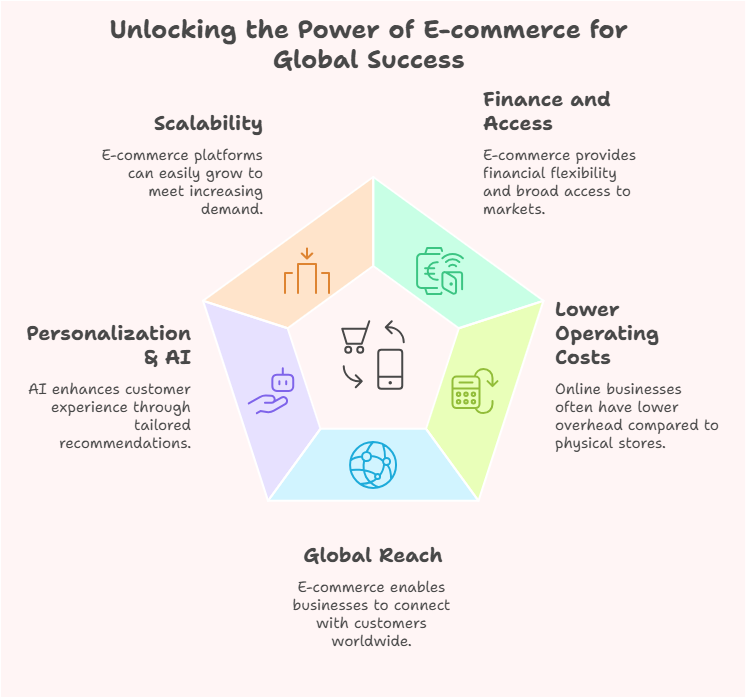
Pros of E-commerce
- Finance and access: buyers can buy goods in the place and when they want, eliminate the need for physical stores.
- Lower Operating Costs: Compared to brick-and-mortar stores, businesses have less rent to pay and can get around the expensive overhead of utility bills, store staff and so on.
- Global Reach E-commerce allows your business to grow and sell products beyond local borders and even overseas.
- Personalization & AI-driven Recommendations: AI-powered tools study customer behavior and provide tailor-made product suggestions, leading to more conversions.
- Faster Transactions & Automation: Payment gateways and automated order processing make transactions seamless and efficient.
- Scalability: Online stores are very easy to scale up without having the physical length of shelves to limit you.
- Data information companies can observe user behavior, draw marketing campaigns and tweak products based on products.
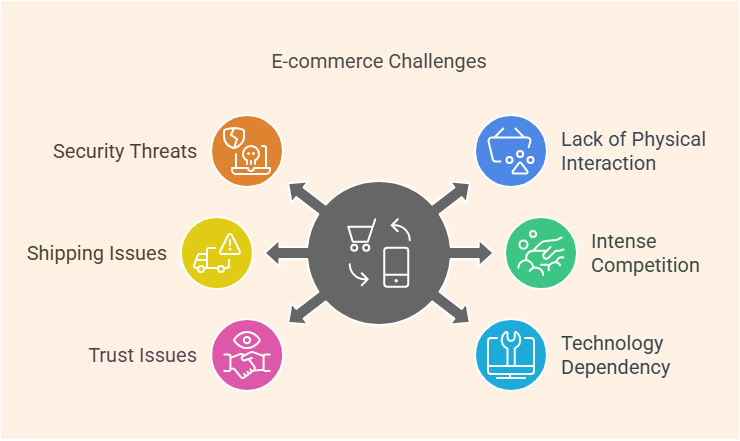
Cons of E -commerce
- Safe and network Menaces: Online stores are at risk of hacking, data violations and debris.
- Lack of Physical Experience: Customers can't touch, try on or feel products before they buy them and so could be disappointed with what's delivered.
- Shipping & Logistics Challenges: This includes problems of high shipping costs, late delivery and returns in the right hands.
- Intense Competition: Businesses must constantly innovate and improve to stay ahead in a market that is awash with players.
- Customer Trust Issues: Small or new e-commerce stores may find it hard to develop credibility without reviews and a known brand reputation.
- Dependency on Technology: Website crashes, payment failures, technical problems can all affect sales and customer experience.
- Legal & Tax Regulations: Selling across borders entails compliance with different tax laws, import / export restrictions and consumer protection policies.
Types of E-commerce Models
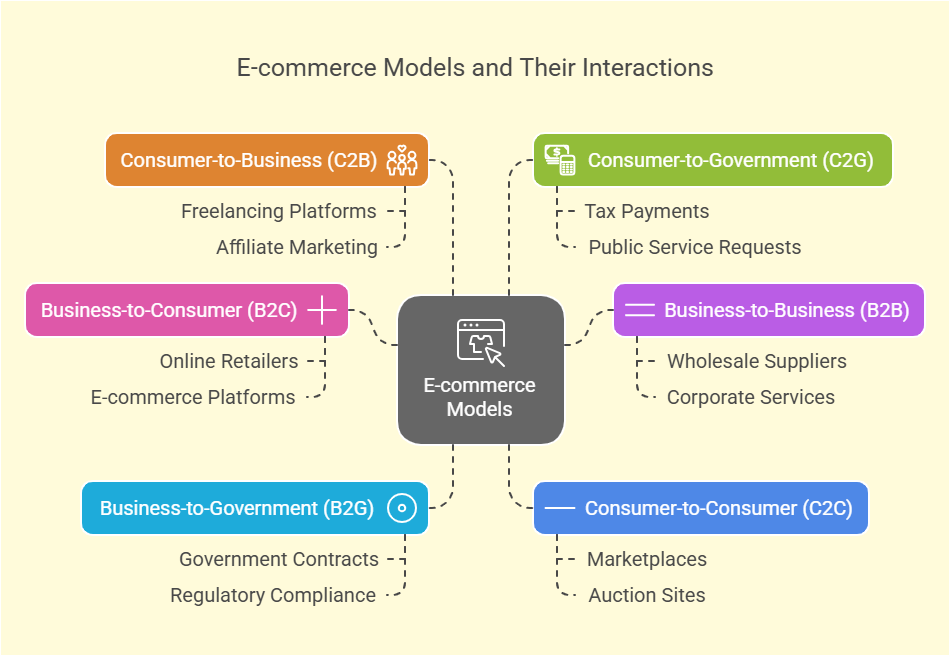
E-commerce Model: Business-to-Customer (B2C)
For example, Amazon offers everything from books to electronics,and H&M sells its own clothing line through its website.
E-commerce Model: Business-to-Business (B2B)
For instance, Grainger sells spare parts and machinery to other companies. When companies sell to other companies special lines are involved.
E-commerce Model: Business-to-Government(B2G)
As an example of such activity might be companies supplying office supplies to central government departments, or technology firms providing specialized equipment for local agencies.
These deals are to get done on your hands and knees These processes often take months many rounds of approvals.
E-commerce Model: Consumer-to-Consumer(C2C)
For example, eBay allows users to auction their things in front of an audience of millions of strangers worldwide who have placed bids for it. Craigslist acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers residing nearby. And Facebook’s Marketplace lets persons sell items within their radius.
E-commerce Model: Consumer-to-Business(C2B)
Upwork brings those working part-time or otherwise available in contact with businesses which need tasks done. And social media platforms have influencers promote items for corporations. These platforms make it easy for businesses to find talented people.
E-commerce Model: Consumer-to-Government(C2G)
The town Web page Ticketmaster makes it possible for customers to pay their parking tickets using Visa or MasterCard, without interminable street-wide preoccupied by soldiers in black leather coats pulling up to the curb as you approach it on foot These platforms are there to make all government services available to everyone as much as possible.
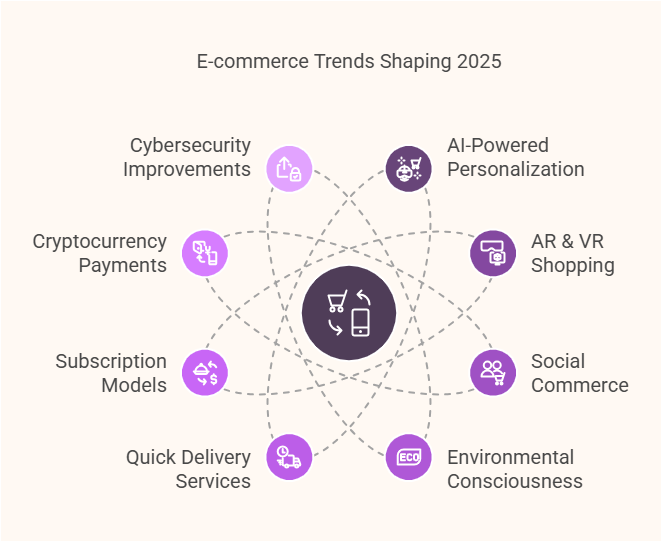
Key Trends Defining E-commerce in 2025
The impact of e-commerce is verifiable, because it has changed how individuals shop by making exchanges less demanding, more convenient, and accessible to a around the world gathering of people.
- AI-Powered Personalization & Shopping Assistants
Manufactured Insights (AI) is revolutionizing e-commerce by advertising hyper-personalized shopping encounters. AI-driven proposal motors analyze buyer behavior, inclinations, and browsing history to recommend important items.
What’s New in 2025?
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual shopping assistants provide real-time support and personalized product suggestions.
- AI-driven content creation enhances product descriptions, images, and marketing campaigns.
Voice and image search capabilities allow users to find products easily.
- Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR) Shopping
AR and VR are bridging the crevice between physical and computerized shopping encounters. Buyers can essentially "attempt on" items some time recently making a buy, decreasing instability and expanding certainty.
What’s New in 2025?
- AR-powered apps allow customers to see how furniture, clothing, or accessories look in real-time.
- Virtual showroom transfers browsing experience for luxury brands.
- VR-based social commerce enables users to join into a hypothetical friends' shopping spree at the mall online.
- Developments in Social commerce and Live Shopping
Independent e-commerce markets involving big consumer brands are emerging on social media platforms such as Instagram, TikTok and Facebook. These kinds of get-togethers/ sales shows that involve influencers and Caigangan have come to be very popular.
What’s New in 2025?
- TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube have enhanced in-app checkout experiences.
- Influencers host live shopping events where viewers can purchase products instantly.
- AI-generated influencers promote products through engaging content.
- Consumers are becoming more environmentally
Conscious and e-commerce brands are now being pressured to adopt sustainable practices. Companies are moving towards eco-friendly packaging, carbon-neutral shipping and acting in accordance with ethics so as not to spoil the source material.
What’s New in 2025?
- Increased use of biodegradable and recyclable packaging by brands.
- All major retailers are now expected to offer carbon-neutral shipping as standard.
- The second hand and reestablished thing market is becoming more grounded.
- Quick Delivery And Same-Day Service Expand
Fast delivery was once a luxury but nowadays, it’s no longer an option. Retailers are setting up micro-fulfilment centers, drone deliveries, and autonomous vehicles in order to address the issue of speedy shipping for their customers.
What’s New in 2025?
- Drones are starting to work as last mile logistics in Urban areas.
- AI in Inventory Management — ensuring the products are available somewhere within storage near by That's great for ops-staff assistants.
- 10-min Delivery Services Growing for Groceries & Essentials.
- The Growth of Subscription Models and Loyalty Programs
Who DOESN'T love a bargain, but convenience is king, and subscription-based e-commerce models have a thing or two to say about that.
What’s Unused in 2025?
- Algorithmic Content Positioned Thing Publicizing Source by through AI Driven Cooperation.
- Membership-based e-commerce (Amazon Prime) Touching borders.
- More reliability from clients gave through extra advantages and offers for early access.
- Cryptocurrency & Other payment forms
Cryptocurrencies and other alternative installment strategies are at last coming into the standard, as shapes of advanced installments advance. Adaptability, security, and instant payment are the shopper favorites.
What’s New in 2025?
- Bitcoin, Ethereum, and stablecoins are widely accepted by online retailers.
- We continue to see expansion on buy now, pay later (BNPL) services such as Klarna and Afterpay
Payments by biometrics (face & fingerprint identity) make it even safer.
- The AI-Based Fraud Detection And CyberSecurity Improvements
Cyber threats are on the rise as e-commerce continues to grow. AI security features also help businesses to secure customer data and repel fraudulent activities.
What’s New in 2025?
- Suspicious activity detection in real time prevent fraud.
- Blockchain technology enhances transparency in transactions.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric logins improve security.
- B2B E-commerce Revolution
Business to business (B2B) e-commerce is closing the gap between business to consumer (B2C), with the need for simplified digital transactions as the most pointed demand from businesses. The growth of online wholesale marketplaces and rise of automated procurement.
What’s New in 2025?
- Smart suggestions: AI-driven suggestions assist businesses in locating the ideal suppliers.
For example, Alibaba’s AI-powered sourcing assistant analyzes historical purchase behavior and supplier ratings to recommend the most reliable and cost-effective vendors in real-time.
- Bulk Self-service B2B portals with custom pricing
- Supply chain transparency goes up with blockchain.
- The Use of Voice Commerce & Smart Assistants
Voice shopping using smart assistants such as Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri is on the rise. Voice command is used by consumers in searching for products, ordering and tracing their delivery.
What’s New in 2025?
- Voice search with AI enhances product discovery.
- E-commerce for Smart Assistants — It means fully integration for hands-free shopping.
- Create less friction in the buying process with voice-based checkout.
Conclusion
AI-powered personalization, AR/VR shopping encounters, maintainable hones, and imaginative installment arrangements are changing the e-commerce industry in 2025. As social commerce and sped-up delivery services are taking precedence along with a greater emphasis on customer experience, online shopping is only going to get more seamless and engaging with time.
In order to stay competitive, businesses need to adapt to these growing trends by utilizing AI-powered insights, sustainable travel, and efficient digital market payment systems. With platforms like 99minds enabling smarter discounting and promotional strategies, businesses can optimize customer retention and loyalty in this evolving landscape.
E-commerce is poised for a future driven by convenience, personalization, and trust—differentiating on the last factor will force brands to innovate, in-between and fast. The future of online shopping in 2025 will offer opportunities and challenges in equal measure for retailers, shop owners, and consumers alike.
Frequently-Ask-Questions-(FAQs) Ecommerce Evolution
What is the future of e-commerce in 2025?
The future of e-commerce in 2025 is shaped by AI-driven personalization, AR/VR shopping experiences, sustainable practices, faster delivery options, and increased adoption of cryptocurrency payments. Brands are leveraging advanced technologies to create seamless, efficient, and engaging shopping experiences.
How is AI impacting e-commerce?
AI is transforming e-commerce by offering personalized product recommendations, automating customer service through chatbots, optimizing inventory management, and enhancing fraud detection. AI-driven insights also help businesses improve their marketing strategies and customer experiences.
What role does augmented reality (AR) play in online shopping?
AR allows customers to visualize products before making a purchase. For example, shoppers can use AR apps to see how furniture fits in their home, try on clothes virtually, or test makeup shades, reducing uncertainty and increasing confidence in their buying decisions. 





